2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) is the other main endogenous cannabinoid that along with anandamide has an effect on the CB receptors in the central and peripheral nervous system. Specifically, 2-AG is a full agonist of both CB receptors, and is the primary ligand (binding molecule) for the CB2 receptor.
Just like anandamide, 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) was discovered in the process of cannabis research. The occurrence of 2-AG in mammals was discovered in mid-90s, in Raphael Mechoulam’s laboratory at the University of Jerusalem. The discovery of both 2-AG and anandamide successfully established the existence of a neuromodulatory system facilitated completely by cannabinoids called the endocannabinoid system.
Chemical structure & properties of 2-AG
2-AG is a member of a group of molecules that derive from arachidonic acid or two other 20-carbon essential fatty acids (EFAs) known as EPA and DGLA. These molecules, known as eicosanoids, are all oxidised versions of these 20-carbon (containing 20 carbon atoms per molecule) EFAs, and play a complex and important role in various bodily processes including immunity and inflammation.
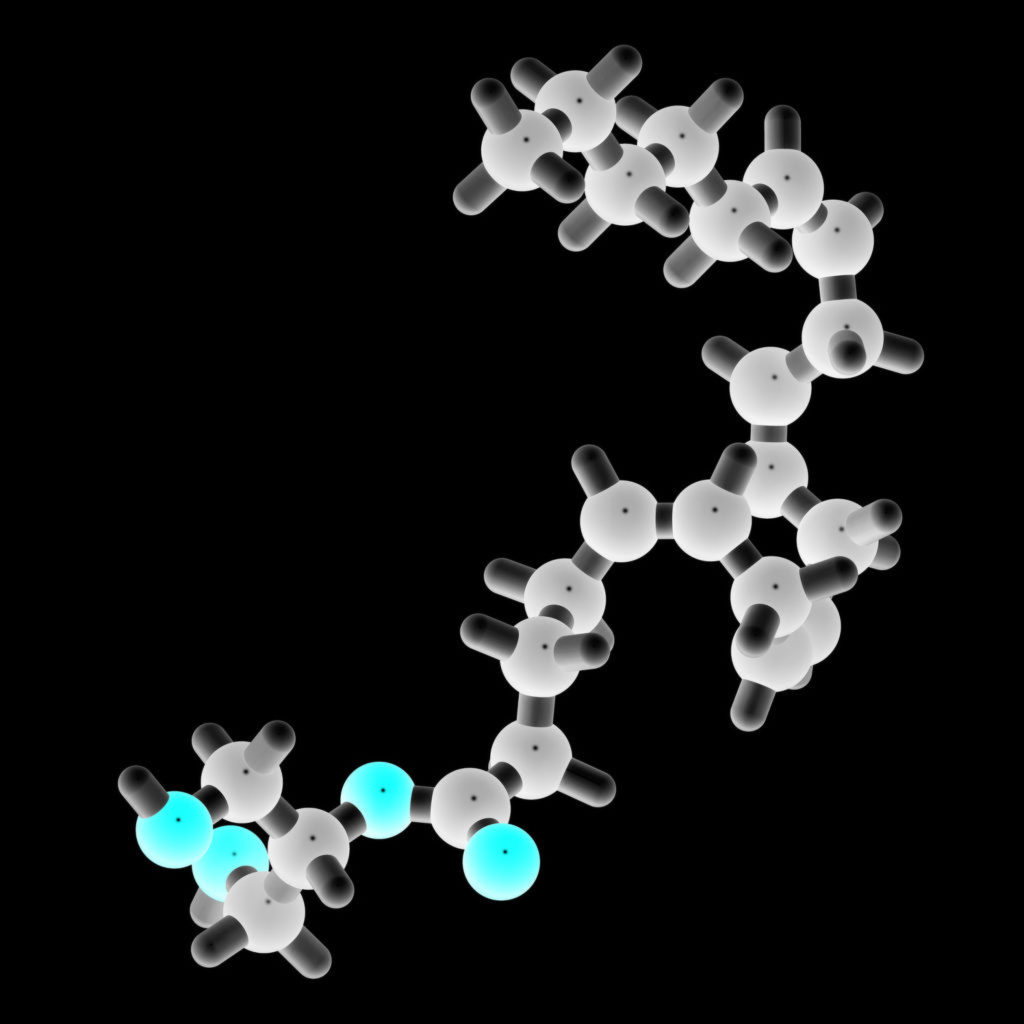
The chemical formula for 2-AG, which can be classed as a fatty acid ester of glycerol as it converts the hydroxyl group of glycerol into a carboxyl group, has the molecular formula C23H38O4 and a molar mass of 378.3 g/mol. Due to its long hydrocarbon tail, the molecule can easily be broken down by the actions of lipid metabolism enzymes.
Synthesis and degradation of 2-AG
2-AG is formed similarly to anandamide—through the reaction of arachidonic acid with another endogenous molecule. However, unlike anandamide, 2-AG requires glycerol rather than a free amine to make the chemical changes required.
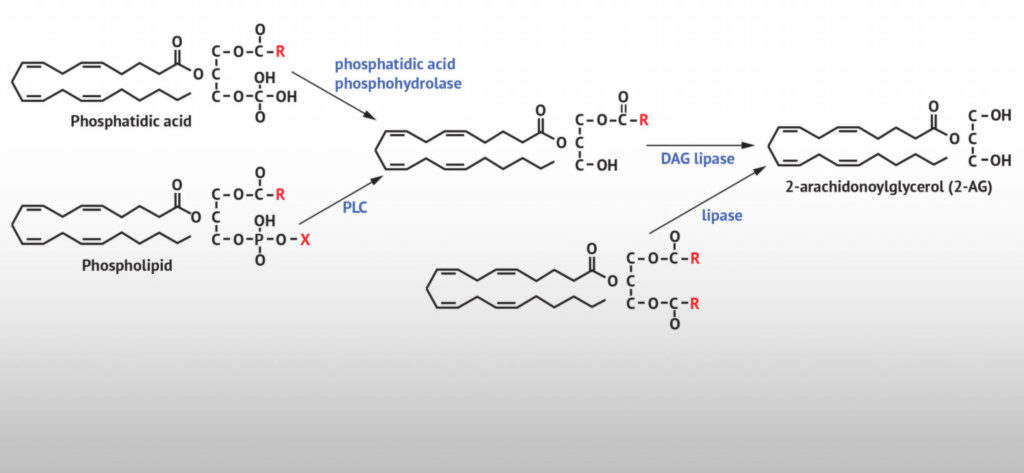
Rather than directly synthesising from the degradation of arachidonic acid, 2-AG is formed when the arachidonic acid-containing phospholipid diacylglycerol (DAG) reacts with glycerol. The enzyme that facilitates this process is known as the DAG lipase.
2-AG is degraded by monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL), fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH, also responsible for the degradation of anandamide) and several uncharacterised enzymes. It is believed that MAGL is responsible for up to 85% of this degradation process.
Physiological effects of 2-AG
2-AG is the most abundant endocannabinoid found in the body, and like anandamide, is thought to play an important role in the regulation of appetite, immune system functions and pain management. It is one of the two most studied endogenous cannabinoids. Given that modern science has only known about the endocannabinoid system since 1992, 2-AG and anandamide may not be the only two.
The full function of 2-AG is yet to be established by modern science, mainly owing to its rapid metabolism in the body. However, it is known that 2-AG plays a vital role in the circulatory system, and either directly or indirectly affects the blood vessels and the heart.
Scientists at the University of Tokyo discovered that 2-AG signalling is an important aspect of seizure suppression. There are various ways for elevating 2-AG levels in the human body, especially using a mechanism that inhibits the enzyme that breaks down 2-AG. Using this technique, researchers found that elevated levels of 2-AG decreased the occurrence of generalized seizures. This suggests a vital role for 2-AG in neurological conditions that affect motor control.
Interestingly, 2-AG has also been found in human breast milk, and in much higher levels than anandamide. Israeli scientists hypothesize that the purpose of 2-AG’s existence in breast milk is to initiate and stimulate the suckling response from an infant to its mothers breast. As most of us are aware, the infant’s life depends on this ability to suck milk from its mother’s breast. The more milk that is released from the breast, the greater the levels of 2-AG which are created in breast milk. This creates a pattern of suckling between the infant and mother which is vital to its survival and development.
2-AG and its relevance to modern medicine
2-AG, along with the rest of the endocannabinoid system, is quickly becoming a target for the treatment of various conditions. Its role in the circulatory system has made it a potential target for cardiac related illnesses, while its effect on neurology makes it a potential target for neurodegenerative conditions.
A lot of scientific attention has been paid to the endocannabinoid system’s role in neurodegenerative conditions. In fact, a dysfunctional endocannabinoid system is hypothesized to be at the root of multiple conditions. Ethan Russo calls this condition Clinical Endocannabinoid Deficiency. 2-AG’s role at the cannabinoid receptor 1 site makes it a potential target for conditions such as Alzheimer’s, Huntington’s Disease, and Multiple Sclerosis. 2-AG is even hypothesized to play a role in the development of schizophrenia, and is being researched as a target for treatment of psychiatric illnesses.
It is clear that 2-AG plays important roles in human physiology, along with its cousin, anandamide. As research continues in the direction of these two endocannabinoids, they continue to become novel targets for a range of different treatments.
- Disclaimer:This article is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult with your doctor or other licensed medical professional. Do not delay seeking medical advice or disregard medical advice due to something you have read on this website.










It seems as if elevated 2-AG is found in heart disease, especially the aorta https://www.hindawi.com/journals/bmri/2015/456582/
“Concentration of the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol was significantly higher, while the second endocannabinoid anandamide and its metabolite arachidonic acid and palmitoylethanolamide were significantly lower in aneurysms.”
Can you please respond with any information on what roles CBD, THC, CBG, or other cannabinoids play in the level of 2-AG and/or anandamide in the aorta?
Thank you for your attention.
Good afternoon Ryan,
I hope you’re having a great day 🙂
Thanks so much for the link, it looks very interesting!
Unfortunately, I’m unable to provide an answer, as it’s outside of our area of expertise.
However, maybe some of our readers will have some ideas?
Have a great day!
Mark
Actually CBGA is the precise analog to 2-AG due to its identical hydrocarbon tail and molecular structure. THC is close… but no cigar. Not in the molecular world.
Good morning Robert,
Thank you for your comment and support.
We’re continuously updating the articles on our blog; I’ve passed your comment to the Sensi team.
The most recent update can be found at the top of the article.
This article on Decarboxylation of CBD and THC– That’s How You Activate Cannabismay be of interest to you.
Thanks again, and I hope you continue to enjoy the blog.
Have a good day,
Mark
Which top 5 stains contain the highest amounts of 2-AG?
Good afternoon Chris,
Thanks for your comment.
Endogenous cannabinoids are cannabinoids produced inside the body. 2-AG is a major endocannabinoid produced by the body which helps maintain homeostasis in the body by activating CB1 and CB2 receptors. Scientifically known as 2-ArachidonoylGlycerol, 2-AG is present in high levels in the central nervous system. It is not found in cannabis flower.
I hope you continue to enjoy the blog.
With best wishes,
Mark
The synthesis of 2-AG is wrong, a phosphatidic acid is not with a carbon atom but a phosphate one after the oxygen on the third glycerol carbon (gamma). And because it’s a phosphate, it has a double bond to the cetone. Source: biochemistry major
Hi Joshua,
Thanks so much for pointing this out! We are currently in the process of overhauling the blog, including fact-checking our existing articles, so we will incorporate your point in the new version where appropriate. In the meantime, I hope you continue to enjoy the blog.
With best wishes,
Scarlet
It appears pretty clear to me that THC is the exogenous equivalent to 2AG.
Life researchco’s Rosin checks all the ECS boxes. Check out CBDinformative’s August 1st review of it spells out why!
Is it 2-AG or the awakening of the CB2?